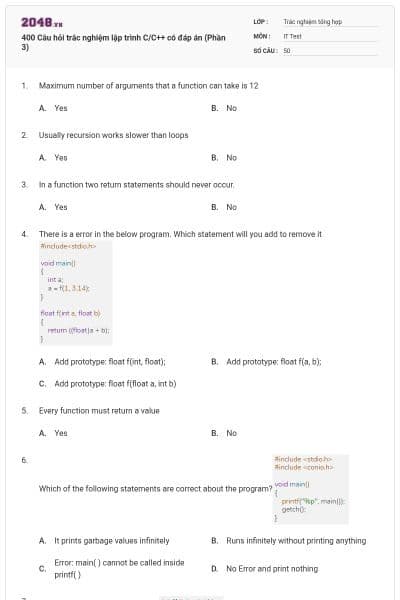
400 Câu hỏi trắc nghiệm lập trình C/C++ có đáp án (Phần 7)
50 câu hỏi
Class members are public by default.
TRUE
FALSE
Friend functions have access only to public members of the class.
TRUE
FALSE
A function designed as public can be accessible by non-members of a class.
TRUE
FALSE
Friendship is commutative.
TRUE
FALSE
New and delete are operators.
TRUE
FALSE
We can implement generic classes using templates
TRUE
FALSE
Using operator overloading we can invent new operators.
TRUE
FALSE
Inheritance helps in making a general class into a more specific class.
TRUE
FALSE
A base class is never used to create objects.
TRUE
FALSE
Classes can be inherited privately.
TRUE
FALSE
It Is legal to return local variables from a function which returns by reference.
TRUE
FALSE
Constructors can be virtual like virtual destructors
TRUE
FALSE
C++ is a pure object oriented programming language.
TRUE
FALSE
In C++ one can define a function within another function.
TRUE
FALSE
A class encapsulates the implementation and interface of a userdefined data type and constitutes an abstract data type.
TRUE
FALSE
In c++ an identifier can begin with a $ sign.
TRUE
FALSE
“My Variable” is a valid identifier in C++
TRUE
FALSE
In C++ one can get the memory addresses of variables and functions.
TRUE
FALSE
%= is not a operator in C++
TRUE
FALSE
std::cout is a standard input stream.
TRUE
FALSE
Preprocessor #define macro and inline functions use the same mechanism.
TRUE
FALSE
All C++ functions are recursive.
TRUE
FALSE
The ‘break’ keyword is only used in the switch..case statement.
TRUE
FALSE
The new operator returns the address and size of the memory block that it allocates.
TRUE
FALSE
The heap storage is used for local objects.
TRUE
FALSE
It is not necessary to initialize a reference to real object when it is declared.
TRUE
FALSE
There can be a null reference.
TRUE
FALSE
One can reassign reference after it is initialized.
TRUE
FALSE
It is nothing wrong that a function returning a reference to an automatic variable.
TRUE
FALSE
One can apply pointer arithmetic with reference variables
TRUE
FALSE
The preprocessor processes source code before the compiler does.
TRUE
FALSE
A class is a basic unit of object-oriented programming.
TRUE
FALSE
A function template defines a parameterized nonmember function, which enables a program to call the same function with different types of arguments.
TRUE
FALSE
Destructors can be overloaded.
TRUE
FALSE
Static data members cannot be private.
TRUE
FALSE
Static member functions can use this pointer.
TRUE
FALSE
One cannot use enumerations in a class.
TRUE
FALSE
One cannot create an object of a virtual class.
TRUE
FALSE
A class that builds a linked list should destroy the list in the class destructor.
TRUE
FALSE
Once an exception has been thrown, it is not possible for the program to jump back to the throw point.
TRUE
FALSE
In C++, only one catch block can handle all the exceptions.
TRUE
FALSE
There can be only one catch block in a program.
TRUE
FALSE
When an exception if throw, but not caught, the program ignores the error.
TRUE
FALSE
A class object passed to a function template must overload any operators used on the class object by the template.
TRUE
FALSE
In the function template definition it is not necessary to use each type parameter declared in the template prefix.
TRUE
FALSE
It is possible to overload a function template and an ordinary (nontemplate) function.
TRUE
FALSE
A class template may not be used as a base class
TRUE
FALSE
When declaring an iterator from the STL, the compiler automatically creates the right kind, depending upon the container it is used with.
TRUE
FALSE
‘ios’ stream is derived from iostream.
TRUE
FALSE
What is the output of the following code?
20,21
20,20
21, 22
none of above